Explore Health Topics That Matter to You
Browse our comprehensive collection of wellness resources
Latest articles
Our recent publications

Compassionate care: philippe jacquet, psychotherapist in london
Are you searching for expert psychotherapy in London that truly understands your unique needs? According to the NHS Engl...

Finding calm: naturopathic treatments for anxiety relief
Anxiety can be overwhelming, but naturopathic treatments offer a holistic approach to finding relief. Explore a variety ...
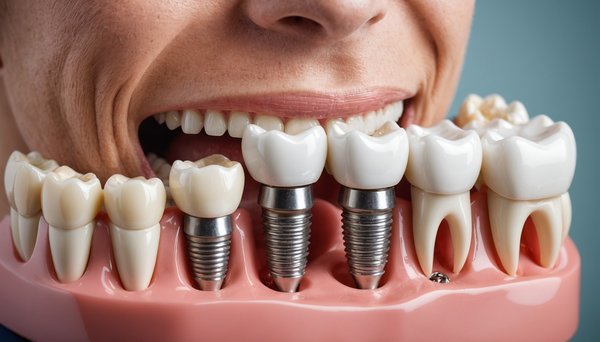
Discover the benefits of dental implants today
Dental implants offer a transformative solution for those seeking to restore their smile and improve oral functionality....

Boosting Mental Wellness: The Impact of Virtual Support Groups on Cancer Survivors
The journey of cancer survivors extends beyond the medical treatments, where addressing mental health becomes crucial. T...

Essential Elements for Crafting an Effective Diet Plan for Teens Facing Type 2 Diabetes
For teens managing Type 2 diabetes, adhering to specific nutritional guidelines is crucial for maintaining health and pr...

Unlocking Wellness: The Transformative Effects of Group Therapy on Individuals with Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder is a complex mental health condition characterized by extreme mood swings that can range from manic hig...

Boost Your Thyroid Health: The Surprising Benefits of Adding Seaweed to Your Diet!
The thyroid function is vital in regulating metabolism and maintaining energy levels. This butterfly-shaped gland, locat...

Boosting Joint Health in Older Adults: The Impact of Regular Water Aerobics Participation
Joint health deterioration is a prevalent issue among older adults. As people age, they often face a variety of joint-re...

Unlocking the Power of Fiber: Does a High-Fiber Diet Enhance Cancer Immunotherapy Outcomes?
When we think about diet and health, one of the often-overlooked but crucial components is fiber. Fiber, particularly di...

Exploring the Impact of Structured Workout Regimens on Fall Risk Reduction in Seniors Living at Home
As people age, the risk of falls becomes a significant concern, impacting not only their physical health but also their ...

Transforming Mental Health Care: Unlocking Access Through Digital Platforms in Underserved Communities
Mental health has become a critical concern in today's fast-paced world. The World Health Organization (WHO) recognizes ...

Unlocking Potential: The Transformative Impact of Adaptive Sports Programs on Individuals with Physical Disabilities
Adaptive sports programs have revolutionized the way individuals with physical disabilities engage in physical activity,...

Effective Strategies for UK Pregnant Women to Thrive in Remote Work Environments
Recent remote work trends in the UK highlight a growing shift towards more flexible employment arrangements. This shift ...

Essential Strategies for UK Expecting Mothers to Prepare for Parental Leave in the Event of Preterm Delivery
When expecting a baby, especially in the event of a preterm delivery, it is crucial for mothers in the UK to understand ...

Ultimate Guide to Selecting Sustainable Diaper Brands in the UK for Eco-Conscious Parents
As an eco-conscious parent, making the right choices for your baby's health and the environment can be overwhelming, esp...

Empowering COPD Management: Innovative Non-Pharmacological Strategies for UK Pulmonologists
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung condition affecting an increasing number of people in...

Tackling the Rise of Childhood Anxiety: Strategies for UK Pediatricians to Make a Difference
Childhood anxiety is a growing concern that affects a significant number of young people in the UK. It is essential for ...

Unlocking Recovery: The Role of UK Neuropsychologists in Stroke Rehabilitation
When a stroke occurs, it can have a profound impact on an individual's life, affecting not only their physical abilities...

Empowering Seniors: Safe and Accessible Yoga Practices for Limited Mobility
For seniors, limited mobility significantly influences their day-to-day activities and overall physical health. It typic...

Exploring the Impact of Lighting on Emotional Well-Being in Seniors Facing Depression
The interplay between lighting and emotional health is a significant concern in everyday life. Lighting conditions can d...

Unlocking Emotional Wellness: A Senior"s Guide to the Power of Journaling
Journaling, a simple yet powerful tool, has been increasingly recognized for its profound impact on emotional wellness, ...

Boost Your Health: Creative Ways to Add Superfoods to the UK Diet
In recent years, superfoods have gained significant attention in the UK due to their supposed health benefits and high n...

Essential Tips for UK Vegetarians to Boost Iron Levels in Their Diet
Iron deficiency is a prevalent concern among vegetarians in the UK. It arises from the body's need for iron, which is of...

Top Non-Dairy Calcium Rich Foods for Lactose-Intolerant Individuals in the UK
Understanding non-dairy calcium-rich foods is essential for those who are lactose intolerant or simply avoiding dairy. T...

Crafting Your Unique Gut Health Enhancement Strategy: A Step-by-Step Guide
A healthy digestive system is crucial for overall wellness. It involves a balance within the gut microbiome, which is a ...

Creating a Sustainable Weight Loss Journey: Your Ultimate Guide to Lasting Results
In the journey to achieving a healthier self, understanding sustainable weight loss is crucial. It involves making healt...

Master the Art of Sleep Hygiene: Your Ultimate Guide to Overcoming Insomnia
Insomnia, a pervasive sleep disorder, affects millions of people worldwide, disrupting their sleep patterns and signific...
Start Your Wellness Journey Today
Explore hundreds of articles, guides, and resources designed to inspire healthier living. Whether you're seeking disease prevention tips, pregnancy advice, or senior wellness insights, find the information you need right here.
Rejoindre →